Whether it's a login page or an internal tool, your React app is going to need a form, and handling events and dataflow via raw HTML inputs isn't any fun. This guide will walk you through how to use the react-hook-form library and take you step-by-step through a project where we create a form for an internal tool and extend it with some useful features.
By the end of this article, you’ll know how to:
- Create a simple form using
react-hook-form - Style your form
- Validate your form
- Add errors to your form
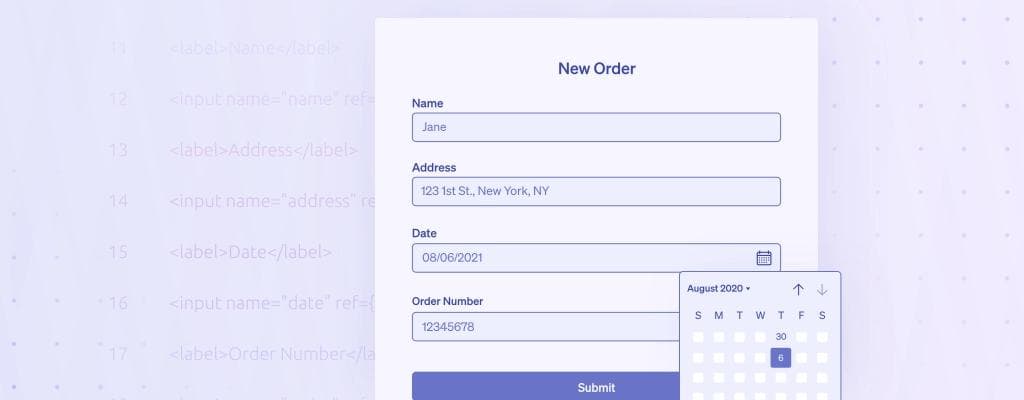
For this tutorial, we're working with a table that lists and orders our data, and has a nifty datepicker for sifting through the orders.

Now, while we know most folks place orders online, we have to recognize that sometimes customers like to order over the phone. This means that we need to give our reps the ability to add new orders to the table.
Our React form component needs to be able to:
- Accept a customer’s name, address, the date the order was made, and an order number
- Validate the data that the customer support rep enters
- Display errors to the rep
Here is what the final product will look and feel like:

First things first, react-hook-form is a library built to handle the data in forms and do all the complicated work with validation, error handling, and submitting. There are no physical components in the library. The form component that we will build will just be made with standard jsx tags.
To start off, we’re going to build a simple form with no styling - it’s going to be a bunch of textarea inputs for the reps to fill out the customer’s name, address, the date of the order, and the order number, and, finally, a plain “submit” button. Keep in mind that react-hook-form uses React Hooks. Hooks are a fairly new feature to React, so if you aren’t familiar, we recommend checking out React’s Hooks at a Glance docs before starting this tutorial.
After you import the useForm() hook, there are basic steps to run through:
- Use the
useForm()hook to getregisterandhandleSubmit().
You need to pass register into the ref prop when you create your form so the values the user adds—and your validation rules—can be submitted. Later on in this tutorial, we will use register to handle validation. handleSubmit() for onSubmit connects your actual form into react-hook-form (which provides register in the first place).
1const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm();
- Create a function to handle your data, so your data actually winds up in your database
Your backend is your own, but we’re going to pretend that we have a saveData() function in another file that handles saving our data to a database. It’s just console.log(data) for the purposes of this tutorial.
- Render your form
We’re creating a React form component, so we will use form-related jsx tags to build it, like <form>, <h1>, <label>, and <input>
Let’s start with a <form> container. Be sure to pass your saveData() function into react-hook-form’s handleSubmit() that you got from the useForm() hook and then into the onSubmit() in the <form> tag. If that sounded really confusing, peep the code below:
1 2 3<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> ... </form>
Next, let’s add a header with <h1> so our reps know what this form is for:
1 2 3<form ...> <h1>New Order</h1> </form>
We’re going to create four <label> and <input> pairs for name, address, date, and order number. For each <input>, be sure to pass register from the useForm() hook into the ref prop and give it a name in the name prop.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" ref={register} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register} />
Finally, we’ll add a submit button by using an <input> with a “submit” type:
1<input type="submit" />
Putting it all together, we will have the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import saveData from "./some_other_file"; export default function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <h1>New Order</h1> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" ref={register} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register} /> <input type="submit" /> </form> ); }
Which will look like this:

Cool, now we have a (kinda) working form.
Subscribe to the Retool monthly newsletter
Once a month, we send out top stories (like this one) along with Retool tutorials, templates, and product releases.
You can easily style your form with CSS modules, styled-components, or your favorite kind of styling. For our tutorial, we’re going to use styled-components.
First, we install and import style-components into our project. Then, we create a styled component (based on a <div>) and plop all of our pretty CSS into that. Finally, we wrap our form in the <Styles> tag to apply the styles. Easy!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import styled from "styled-components"; import saveData from "./some_other_file"; const Styles = styled.div` background: lavender; padding: 20px; h1 { border-bottom: 1px solid white; color: #3d3d3d; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 20px; font-weight: 600; line-height: 24px; padding: 10px; text-align: center; } form { background: white; border: 1px solid #dedede; display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: space-around; margin: 0 auto; max-width: 500px; padding: 30px 50px; } input { border: 1px solid #d9d9d9; border-radius: 4px; box-sizing: border-box; padding: 10px; width: 100%; } label { color: #3d3d3d; display: block; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; font-weight: 500; margin-bottom: 5px; } .error { color: red; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 12px; height: 30px; } .submitButton { background-color: #6976d9; color: white; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; margin: 20px 0px; `; function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" ref={register} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register} /> <input type="submit" className="submitButton" /> </form> ); } export default function App() { return ( <Styles> <Form /> </Styles> ); }
That’s a lot of styling code, but look where it gets us!

If you hate battling CSS, using a React component library might be a good option. It can add a lot of functionality, like animations, that are time-consuming to implement. If you’re not familiar with the plethora of React component libraries, you can check out our recent post that covers our favorites. For this example, we’re going to use Material UI.
The easiest way to incorporate a React component library is to use one that exposes the ref field as a prop. Then, all you have to do is substitute it for the <input> field and then pass register to that ref.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20import { Button, TextField } from "@material-ui/core"; ... function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <> <h1>New Order</h1> <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Name</label> <TextField name="name" inputRef={register} /> ... // Let's use Material UI's Button too <Button variant="contained" color="primary">Submit</Button> </form> </> ); }
Now, we get the sleekness and functionality of Material-UI.

The last thing we want is for our customer support reps to add faulty data into our database. If we have any other apps using the same data, like reports running on the number of orders made in a certain time span, then adding in a date that isn’t formatted correctly could ruin the whole thing.
For our use case, we are going to add validation in the form of:
- Making all fields required
- Adding an address validator
- Validating date
- Validating order number
All you have to do to make a field required is pass an object into the register() prop in input that says {required: true}.
1<input name="name" ref={register({ required: true })} />
This will flag the errors prop for the “name” field, which can then be used to add an error message (see next section).
To make our life easy, we are going to add a validator to check whether the address the user enters exists and is properly formatted.We’ll use a mock function from our example and show you how to integrate it into the React form component.
First, we define our validator function. For our purposes, we are just checking a specific string. This is where you would hook into your validator library.
1 2 3 4 5 6function addressValidator(address) { if (address === "123 1st St., New York, NY") { return true; } return false; }
Next, we add validation to the register for address input. Make sure to pass the “value” that the user enters. If your validator function returns true, then it is validated and no error will appear.
1 2 3 4<input name="address" ref={register({ required: true, validate: value => addressValidator(value), })} />
If you want to go further with your address validation than just adding a mock function (which you probably do because this is useless in production), we recommend checking out this awesome tutorial from HERE on validating location data.
To make sure users only enter valid dates into our date input field, we're going to add type="date" to our date input field in the React form component in order to force the user to fill out the field in our specified format.

In some browsers (like Chrome), this will add a DatePicker to the input box. In all browsers, it will provide a clear format for the date the rep should enter and will not let them use a different format. We can even add a max date to stop the customer support rep from accidentally adding a future order date (as much as we’d all love to just skip 2020).
For this section, we’re going to use the moment library since it makes formatting dates much easier than JavaScript’s native date.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9import moment from 'moment'; ... <input name="date" type="date" max={moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD")} ref={register({ required: true })} />
The cool thing about validating the date in the input as opposed to the register is that we won’t have to waste time and energy building out error messages since the input will stop our user from entering an erroneous value.

Looking good!
For our order number field, we need to add validation that ensures the input is a valid order number in our system. react-hook-form has a really easy way to apply regex validation by passing a “pattern” into the register.
Let’s say that our order numbers are always 14 integers long (though this regex could easily be updated to fit whatever your order numbers look like).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9<input name="order" ref={register({ required: true, minLength: 14, maxLength: 14, pattern: /\d{14}/, })} />
Great work! Now an error will bubble up when the order number does not meet our specified pattern. For more details, you can read more in the register section of the react-hook-form documentation.
Adding error handling to your form is easy with react-hook-form. Let’s start with communicating that certain fields are required. All we have to do is get errors from the useForm() hook and then add a conditional to render them under the input if they are needed.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39function Form() { const { register, errors, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <h1>New Order</h1> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register({ required: true })} /> {errors.name && "Required"} <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register({ required: true, validate: value => addressValidator(value) })} /> {errors.address && "Required"} <label>Date</label> <input name="date" type="date" max={moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD")} ref={register({ required: true })} /> {errors.date && "Required"} <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register({ required: true, pattern: /\d{14}/, })} /> {errors.order && "Required"} <input type="submit" /> </form> ); }
Notice how we refer to the error for a specific input field by using errors.name and errors.date. And here is what our error looks like:

One last issue - since these errors are conditionals, they’ll increase the size of our form. To get around this, we will make a simple error component that renders the height of the error, even if there is no text. We’ll also color the text red, so it’s easier to see.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import styled from "styled-components"; import saveData from "./some_other_file"; const Styles = styled.div` background: lavender; ... .error { color: red; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 12px; height: 30px; } `; // Render " " if no errors, or error message if errors export function Error({ errors }) { return <div className={"error"}>{errors ? errors.message : " "}</div>; } export function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <h1>New Order</h1> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register({ required: true })} /> <Error errors={errors.name} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register({ required: true, validate: value => addressValidator(value) })} /> <Error errors={errors.address} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" type="date" max={moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD")} ref={register({ required: true })} /> <Error errors={errors.date} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register({ required: true, pattern: /\d{14}/, })} /> <Error errors={errors.order} /> <input type="submit" className="submitButton" /> </form> ); } ...
But wait! There’s no error message text to render. To fix this, let’s start with the Required validation. We do this by adding the error message for that particular type of error.
1<input name="name" ref={register({ required: 'Required' })} />
Go through your code and change required: true to required: 'Required' in every place that you see it. Now this functions a lot more like a form we would expect to see in the real world:

But hold on! We validated a lot more than just required fields. Let’s get a little more granular with these errors, so our customer support reps know how to fix the problem.
To add an address error to your validate section, simply add an || so that if your validation function returns “false,” it will display your message instead.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7<input name="address" ref={register({ required: 'Required', validate: value => addressValidator(value) || 'Invalid address', })} />
Here is what your error will look like:

In our system, our order numbers are always 14 digits long and made up of positive integers between 0-9. To verify this order number pattern, we are going to use minLength and maxLength to verify length and pattern to verify the pattern.
First, change “minLength”, “maxLength”, and “pattern” into objects with a value key, where the regex pattern or number you defined is the value, and a message key, where the value is your error message.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18<input name="order" ref={register({ required: 'Required', minLength: { value: 14, message: 'Order number too short', }, maxLength: { value: 14, message: 'Order number too long', }, pattern: { value: /\d{14}/, message: "Invalid order number", }, })} />
Here is what your error will look like:

And that’s it for errors! Check out react-hook-form’s API docs for more information.
Here is our final React form component:

For more code samples that cover the vast range of features that react-hook-form has to offer, check out React Hook Form’s website. And for a full version of this code that you can test out and play around with, check out our code sandbox.
We know that this tutorial covered a ton of features for forms in react-hook-form, so just to make sure you didn’t miss anything, here is a roundup of the features we covered:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import saveData from "./some-other-file"; export default function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Field</label> <input name="field" ref={register} /> <input type="submit" /> </form> ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import styled from "styled-components"; import saveData from "./some_other_file"; const Styles = styled.div` background: lavender; padding: 20px; h1 { border-bottom: 1px solid white; color: #3d3d3d; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 20px; font-weight: 600; line-height: 24px; padding: 10px; text-align: center; } form { background: white; border: 1px solid #dedede; display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: space-around; margin: 0 auto; max-width: 500px; padding: 30px 50px; } input { border: 1px solid #d9d9d9; border-radius: 4px; box-sizing: border-box; padding: 10px; width: 100%; } label { color: #3d3d3d; display: block; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; font-weight: 500; margin-bottom: 5px; } .submitButton { background-color: #6976d9; color: white; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; margin: 20px 0px; } `; export function Form() { const { register, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Field</label> <input name="field" ref={register} /> <input type="submit" className="submitButton" /> </form> ); } export default function App() { return ( <Styles> <Form /> </Styles> ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register({ required: true })} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register({ required: true, validate: value => addressValidator(value) })} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" type="date" max={moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD")} ref={register({ required: true })} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register({ required: true, pattern: /\d{14}/, })} /> <input type="submit" /> </form>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11export default function Form() { const { register, errors, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <label>Field</label> <input name="field" ref={register({ required: true })} /> {errors.name && "Name is required"} </form> ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134import React from "react"; import { useForm } from "react-hook-form"; import styled from "styled-components"; import moment from 'moment'; import saveData from "./some_other_file"; const Styles = styled.div` background: lavender; padding: 20px; h1 { border-bottom: 1px solid white; color: #3d3d3d; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 20px; font-weight: 600; line-height: 24px; padding: 10px; text-align: center; } form { background: white; border: 1px solid #dedede; display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: space-around; margin: 0 auto; max-width: 500px; padding: 30px 50px; } input { border: 1px solid #d9d9d9; border-radius: 4px; box-sizing: border-box; padding: 10px; width: 100%; } label { color: #3d3d3d; display: block; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; font-weight: 500; margin-bottom: 5px; } .error { color: red; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 12px; height: 30px; } .submitButton { background-color: #6976d9; color: white; font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; margin: 20px 0px; } `; export function addressValidator(address) { if (address === "123 1st St., New York, NY") { return true; } return false; } export function Error({ errors }) { return <div className={"error"}>{errors ? errors.message : " "}</div>; } export function Form() { const { register, errors, handleSubmit } = useForm(); return ( <form onSubmit={handleSubmit(data => saveData(data))}> <h1>New Order</h1> <label>Name</label> <input name="name" ref={register({ required: 'Required' })} /> <Error errors={errors.name} /> <label>Address</label> <input name="address" ref={register({ required: 'Required', validate: value => addressValidator(value) || 'Invalid address', })} /> <Error errors={errors.address} /> <label>Date</label> <input name="date" type="date" max={moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD")} ref={register({ required: 'Required' })} /> <Error errors={errors.date} /> <label>Order Number</label> <input name="order" ref={register({ required: 'Required', minLength: { value: 14, message: 'Order number too short', }, maxLength: { value: 14, message: 'Order number too long', }, pattern: { value: /\d{14}/, message: "Invalid order number", }, })} /> <Error errors={errors.order} /> <input type="submit" className="submitButton" /> </form> ); } export default function App() { return ( <Styles> <Form /> </Styles> ); }
react-hook-form has nearly 35K stars on GitHub, but it's worth taking a second to explain why we decided to go with react-hook-form instead of other popular React form libraries, like formik and react-final-form. It’s worth recognizing that these form libraries are pretty awesome in their own ways:
formikhas top-notch documentation and extremely thorough tutorials.react-final-formis great for those used to working withredux-final-form.
Ultimately, we chose react-hook-form because it has a tiny bundle size, no dependencies, and is relatively new (many sources, like LogRocket and ITNEXT, are claiming it is the best library for building forms in React) compared to the rest. If you’re interested in learning about some other ways to build React forms, check this out.
Reader